
"Males and females often experience different optima in mating rate, which may cause evolution of female resistance to matings and male counter adaptations to increase mating rate." - Hansen et al

The adaptive value of tonic immobility as a form of thanotosis is straight forward. When the state is induced, an animal is not simply lying as still as possible to feign death, it physically cannot move. Thus, as a type of thanotosis, tonic immobility would be most believable, and thus most effective.
In many spider species, procreation can be fatal. Females tend to eat their mates. Research shows that male Pisaura Mirabilis (a species of nuptial gift-giving spider) use thanotosis in mating as an antipredation technique against their female counterparts. Those that perform thanotosis are more successful in mating than others. (Hansen et al 2007)
Content Warning: Sexual Assault
The most studied area of tonic immobility in humans is that of sexual assault victims. Steven Taylor says that "Some rapists may become extremely violent if the victim fights back, and therefore tonic immobility may save the life of the assault victim. In some cases, tonic immobility may even abort the sexual assault, because some rapists lose interest in victims who are immobile and unresponsive." (Taylor 2006) The adaptive value of tonic immobility in humans, as in other animals, can be the difference between life and death (Marx 2008).
Adaptive Value
While the most blatant and well known examples of tonic immobility lay in studies of sharks, chickens, and other non-human creatures, we must not forget that humans too are animals.
Tonic immobility in humans is an adapted defensive reflex. Similar to the other cases of tonic immobility as thanotosis that have been discussed, some predators forgo their prey if it appears dead. In such predator-prey situations, the adaptive value of tonic immobility in humans is apparent. (Taylor 2006)
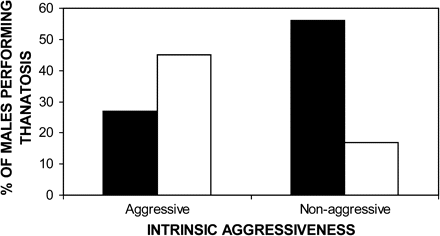
Figure 6. Percentage of control and handicapped males performing thanatosis in trials with intrinsic aggressive and less-aggressive females. Filled bars, control group; open bars, handicapped group.
